Does Cat6 Ethernet Cable Have Slow Upload Speeds?

Did you know that an ethernet cable tin drastically dull your internet speed?
Ethernet cables are often an disregarded attribute of a domicile network. Many people use them every day without thinking about information technology. This is dangerous, because ethernet cables can have a straight affect on their cyberspace speed.
Granted, ethernet cables tin exist confusing because they come in a variety of types and categories, but information technology's important to know that some are better than others depending upon what you're using them for.
The skillful news for y'all? We're going to take a deep dive into the different types of ethernet cables. Not simply that, but I volition detail what these cables are used for and how you can tell what type you lot are using.
What do ethernet cables look like?
Does this look familiar?

The above flick is a CAT5e ethernet cable. The other end of the cablevision looks identical to the end yous run across here (which is a male person RJ45 connector). As you will notice out, the vast majority of ethernet cables volition look like this.
Now that nosotros know what these cables await similar, let's dig deeper to find out what they're used for.
What do ethernet cables do?
Ethernet cables are used to connect computers to the net with a wired connexion.
Additionally, ethernet cables tin can be used for communication betwixt computers and other devices such as printers and fax machines. They're also used to connect your modem to your router (if they are separate devices). To provide a visual of what a dwelling house network might await like:
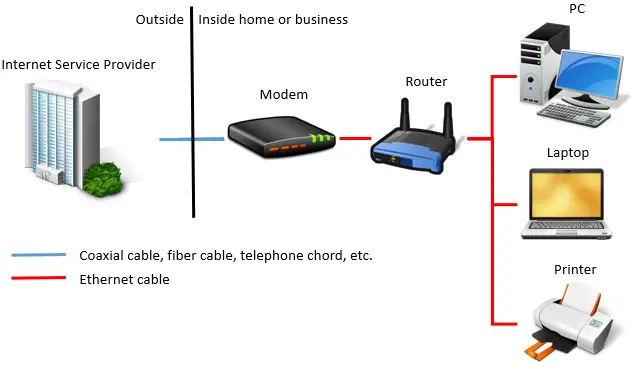
As you can come across, ethernet cables tin exist used for a majority of the devices in your home.
Why should ethernet cables exist used?
Ethernet connections offer a more than reliable connection than if y'all were to wirelessly connect your devices.
Wireless connections (i.east. WiFi) are subject to interference that ethernet connections don't feel (due east.g. walls, other electronic devices using the aforementioned radio channel, etc.). In fact, your internet connectedness will be faster over ethernet than if y'all were to utilize a wireless connexion.
But simply if yous use the correct cables.
I know what you are thinking:
What's the big deal? It's merely a cable. How can it play such a big cistron in my internet speed?
How can an ethernet cablevision slow your internet speed?
As of this writing, ethernet cablevision speeds of up to 10 Gbps tin be expected, while the newest versions of WiFi tin only offer maximum speeds of 867 Mbps (802.11ac) and 150 Mbps (802.11n). That is a pregnant deviation.
Information technology is of import to notation hither that simply using ethernet cables will not event in ten Gbps net. You demand to brand sure you accept the proper internet equipment in your home. Yous also demand to make certain you are getting sufficient bandwidth from your Internet Service Provider (Isp).
The most important aspect of ethernet cables is you lot need to brand certain they are non the clogging of your network.
What exercise I mean by this?
What is an case that will assistance me visualize this?
Moving-picture show your dwelling internet like a organization of h2o pipes. If the water flow from the street is 20 gallons/minute only your pipes can but handle 5 gallons/infinitesimal of water, your shower will only receive 5 gallons/minute of water. The pipes in this instance are your ethernet cables, and your shower is your device (laptop, smart TV, etc.)
Perhaps a diagram volition help y'all visualize this:
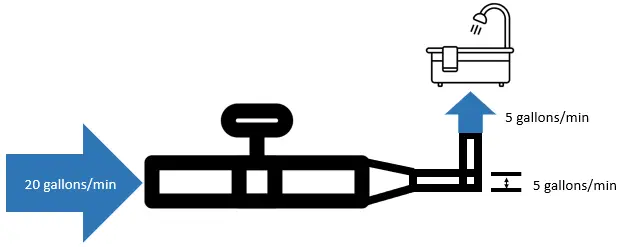
The point here is that if y'all are paying for gigabit net (1 Gbps) only your ethernet cables tin but support 10 Mbps, your device will just take admission to 10 Mbps. You cannot force data through the cables faster than what they are designed for.
Let's employ the water pipe example again. If the period of water from the street is 5 gallons/minute and your pipes are able to handle 20 gallons/minute of water flow, your shower volition only take five gallons/infinitesimal of water flow.
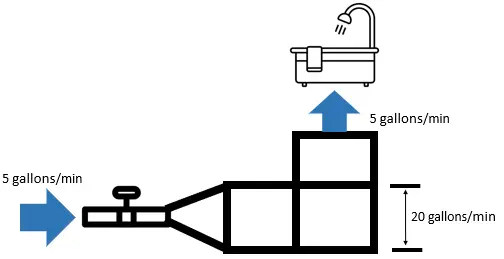
The pipes don't increase the flow of h2o. If you desire to optimize the catamenia of water to your shower, the pipes in your house need to be designed for the flow of water coming from the street.
How does this apply to ethernet cables?
The same is true for ethernet cables. You lot need to ensure they tin can support the bandwidth (i.east. speed) that is existence provided to you lot by the ISP. Ethernet cables don't brand your internet faster, but they sure can slow information technology down if the wrong cables are used.
Make sense?
In order to determine what speeds your ethernet cables need to support, yous need to await at:
- The speed of the internet program that you are signed up for
- The bandwidth supported by delivery devices (eastward.g. modem and router)
- The bandwidth needed for your devices to function properly (eastward.yard. smart T.V., laptop, etc.)
I will brand this process very easy for you, but first let's take a look at the types of cables available.
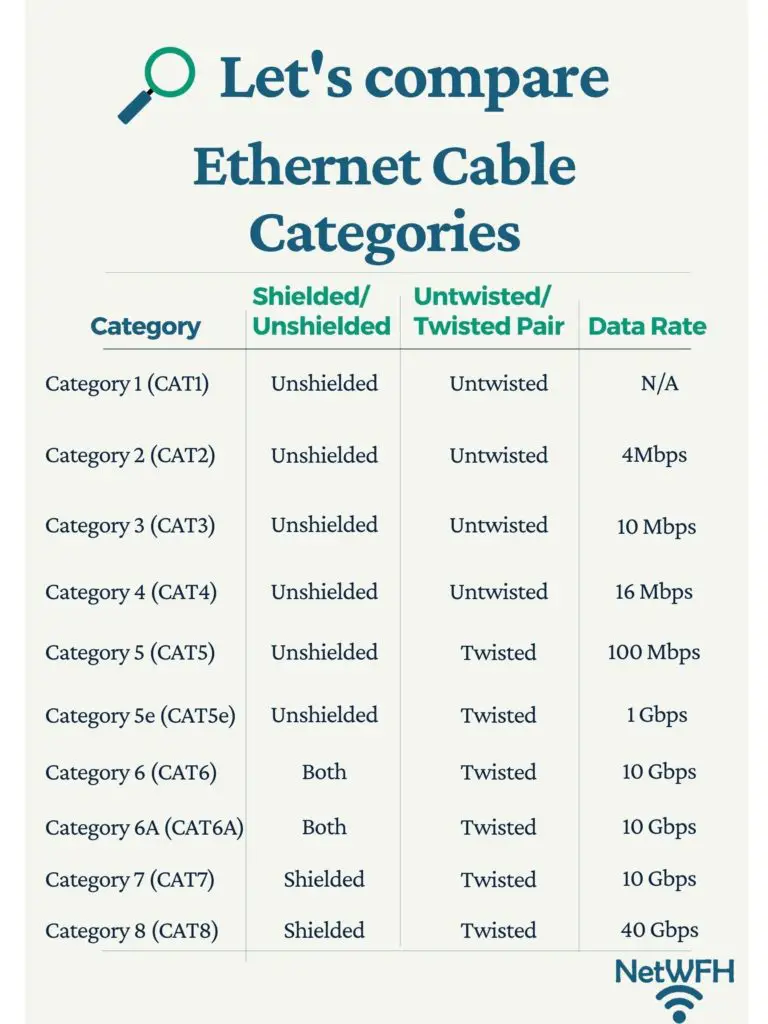
Types of ethernet cables
There are multiple categories of ethernet cables. Some categories are no longer used and as a result I will simply go over them briefly. The categories you should pay attention to are the ones that are in apply today, and the ones that will be used in the futurity.
Let's become started:
Category i (CAT1)
CAT1 ethernet cables are no longer used. They were previously installed in analog telephone wire installations prior to 1983. At the fourth dimension, they were only designed to conduct vox communications. This makes them unusable in figurer networking applications.
What'southward more, the organizations that institute the standards for the ethernet cable categories (TIA/Environmental impact assessment) do non officially recognize CAT1 cables.
Should I use CAT1 cables in my network?
No. This above groundwork is only for your information. You volition non need to use CAT1 cables in your internet network. In fact, I will be shocked if you come across CAT1 ethernet cables in your travels.
Category 2 (CAT2)
CAT2 ethernet cables are an comeback over CAT1 cables, but only marginally.
Different CAT1 ethernet cables, CAT2 cables are designed for reckoner networking and digital voice communication. The bad news is they support very low speeds (upward to 4 Mbps) for computer communication. This is molasses in today's world.
Similar to CAT1 cables, the TIA/EIA did not establish standards for CAT2 cables as an official ethernet category.
Should I use CAT2 cables in my network?
No. As you can guess, these cables are no longer used for networking. Nevertheless, y'all may still be able to find them in some (really) old telephone systems today.
Category iii (CAT3)
CAT3 cables were introduced in the early 1990s and were widely used in local area networks (LANs). In simpler terms, CAT3 cables were used to connect computers and devices to allow for communication between them.
They enabled data manual rates up to x Mbps, which was more than double what CAT2 cables could provide. The speed of CAT3 cables was a large comeback at the time, but their dominance was short lived; in the mid 1990s superior cables were developed and CAT3 cables were replaced.
CAT3 cables are recognized past TIA/EIA as an official ethernet cable category. They were the offset category of ethernet cable that the group developed standards for.
Should I utilize CAT3 cables in my network?
No. Although these cables were improvements over the ones that came earlier them, you lot will not encounter them in use today. 10 Mbps will not support the speeds required in today's world.
Category 4 (CAT4)
Although category 4 cables were developed for reckoner communications, they ended up existence used more in telecom-based communications.
They supported faster speeds than CAT3 cables (up to xvi Mbps) but never gained traction in the computer networking world. As a event, you will only find them in very quondam communications systems that take non been recently upgraded.
Although CAT3 cables were recognized by TIA/EIA as an official category of ethernet cables, CAT4 cables were non.
Should I use CAT4 cables in my network?
No. You will very probable never cantankerous paths with CAT4 cables, and there are much better options available to you. Even if they were widely used, you would not desire to use them because you will need information rates faster than sixteen Mbps.
Category 5 (CAT5)
When CAT5 cables were adult, they were a huge upgrade over previous ethernet cables. They support speeds up to 100 Mbps. This was a huge upgrade in performance at the time.
Different CAT4 cables, they were widely used for computer communication in the 1990s. They were developed for telephone and video signals as well, merely they were mostly used for computer networks.
TIA/EIA recognized CAT5 cables as an official category, although they published a newer CAT5 standard in 2001.
Should I apply CAT5 cables in my network?
Almost probable not. Equally I'thou sure yous can guess, ameliorate performing ethernet cables have been developed and CAT5 cables have mostly been replaced as a result. Although 100 Mbps is not horrible, you lot tin find inexpensive alternatives that provide significantly higher performance. I would suggest you to use improve cables in your network.
Category 5e (CAT5e)
As mentioned in the previous department, the CAT5e standard was adult in 2001 to provide improvements to CAT5 cables. This category of cable provides performance improvements over CAT5 cables, likewise as faster data rates. CAT5 cables had issues with crosstalk, which is caused by the alignment of the wires within the ethernet cable. Crosstalk was minimized by twisting the wire pairs inside the cables, which we will get to later.
CAT5e cables enable data rates of up to i,000 Mbps (1 Gbps).
Should I use CAT5e cables in my network?
Yes. Now we are talking. 1,000 Mbps is a sufficient data charge per unit for many home networks, even if you have cobweb net. This is widely used in many businesses and home internet setups, and will be a good option for nearly people. I utilise CAT5e cables in my home network, as well as CAT6 cables (read on!).
Category 6 (CAT6)
CAT6 ethernet cables accept CAT5e cables to some other level. Like to CAT5e cables they are assembled to minimize any crosstalk interference that may occur by twisting the cable pairs. To further reduce interference, CAT6 ethernet cables have two mechanisms for providing additional insulation to the cables:
- Including an insulating spline in the center of the cablevision to further divide each individual wire
- Providing foil shielding for each individual pair of twisted wires in the cable
Category half-dozen cables are rated for speeds upward to 10 Gbps at curt distances, so they are faster than CAT5 cables as well.
Many datacenters, government websites, and hospitals utilize CAT6 cables every bit a result of their massive data transfer needs.
TIA/Eia has developed the standards for CAT6 cables and recognize it every bit an official category of ethernet cablevision.
Should I use CAT6 cables in my network?
Yep. CAT6 cables enable information speeds that are about probable more than what you would need at domicile. That being said, they are not extremely expensive. They will allow you to "future proof" your net because cyberspace speeds will continue to increase in the time to come and yous know yous will not have to replace your ethernet cables when that happens. I have some CAT6 cables in my home network for this reason.
In curt, yous tin can't become wrong using these cables for your network as long as you are willing to spend some extra money for them.
Category 6A (CAT6A)
CAT6A cables take CAT6 cables a step further. The "A" in CAT6A stands for "augmented" as they're an improvement over CAT6 cables. The differences between CAT6 and CAT6A are equally follows:
- CAT6A cables support the same data rates equally CAT6 (up to 10 Gbps), just over longer distances (up to 100 meters). CAT6 cables support x Gbps up to 55 meters.
- CAT6A cables are congenital to tighter specifications than CAT6 cables. This further prevents potential crosstalk in the wires.
- CAT6A cables are thicker than CAT6 cables, which makes them less flexible. Less flexible cables makes information technology harder to install them in tight spaces (like offices). It also makes CAT6A cables more expensive to install than CAT6 cables.
TIA/EIA revised the CAT6 cable standard in 2008, leading to the introduction of CAT6A.
Should I use CAT6A cables in my network?
Most likely non. If you are setting up a dwelling house network or small function, CAT6A will probably be overkill. In most recreational cases you will not need ethernet cables longer than 55 meters.
This is the reason why I use CAT6 cables in my home network and not CAT6A; I only need about ten anxiety of ethernet cable and CAT6 cablevision supports the same data rates. At that place was no reason for me to spend the extra money on CAT6A cables.
Category 7 (CAT7)
Y'all may retrieve that Category vii cables are an improvement over CAT6A cables, but information technology is actually the opposite. The standard for CAT7 cables was developed in 2002 (before CAT6A standards were established).
CAT7 cables were adult as a standard by a group of companies, and not by TIA/EIA like well-nigh other cables. Equally a result, there are several differences between CAT7 cables and CAT6:
- These cables don't use the traditional RJ45 connector that most other cables utilise. CAT7 cables utilize the GG45 connector which is backwards uniform with RJ45 connectors
- They have stricter specification requirements for limiting crosstalk
- They enable the same data rates as CAT6 cables (upwardly to 10 Gbps) just for upwardly to 100 meters
The It industry did not widely adopt CAT7 cables because of their GG45 connectors. The TIA/EIA developed CAT6A standards to account for this.
What is an RJ45 Connector?
For your reference, this is what an RJ45 connector looks similar:
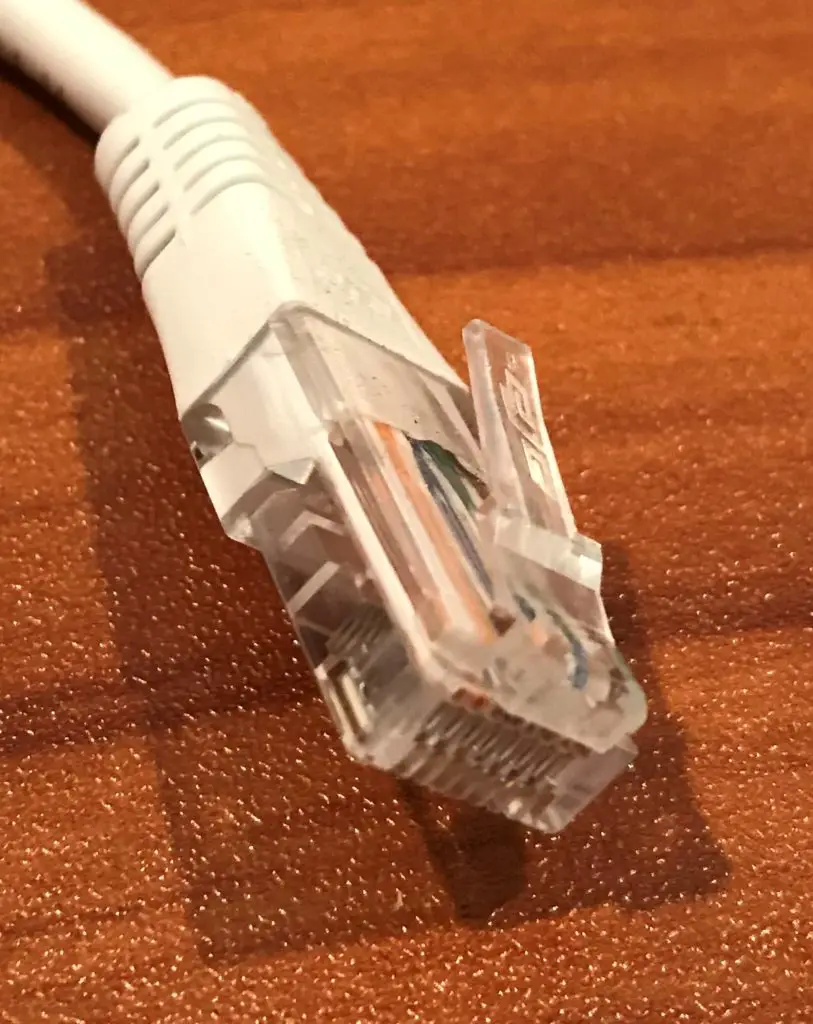

CAT6A cables provided the same functioning specifications as CAT7 cables merely they used RJ45 connectors. In addition, the Information technology community felt more comfy with CAT6A cables because TIA/EIA signed off on them equally an approved ethernet cable standard. As a result CAT6A cables were widely adopted and CAT7 cables were not.
Should I use CAT7 cables in my network?
No. Exercise not permit the fact the fact that CAT7 seems meliorate or newer than CAT6A fool you lot. If you demand high information rates in your network over a long altitude (up to 100 meters), become with CAT6A cables. You volition want the same connector on all your ethernet cables for simplicity.
That being said, CAT6A/CAT7 specifications will be overkill in most applications.
Category viii (CAT8)
CAT8 cables enable the fastest data rates. They can support speeds upwardly to xl Gbps for up to 30 meters. Although they are faster than all other cables, they support data rates over shorter distances.
They are an IEEE standard (non TIA/EIA) that uses RJ45 connectors similar well-nigh other cables. They are designed for use in datacenters as a result of the data rates they support. The cables are configured to well-nigh eliminate crosstalk. Their configuration makes them the hardest to install in tight spaces considering they are not flexible.
Should I use CAT8 cables in my network?
No, unless you are looking to configure a information center. CAT8 cables are generally used betwixt switches in datacenters, which tin can't afford interference. This type of cable will not be your best choice in any other application.
Ethernet Cable Configurations
When looking to purchase ethernet cables, you lot will most probable see the terms "twisted pair", "untwisted pair", "shielded", and "unshielded". It is important to know the differences between the operation of these configurations.
Untwisted Pair Cable
In all ethernet cables used today (CAT5 and higher up), the wires in an ethernet cable are twisted. This helps reduce interference between the wires in the cable. Each wire has electricity running through it, which creates a magnetic field in the cable and can interrupt the electric signals in the other wires next to it.
To visualize this, await at the image below. In an untwisted pair configuration, the pairs of wires blueish-white, orange-white, etc. would not be twisted together. They would simply exist side-past-side within the cable.
Y'all will not come across untwisted cables used today and so this is simply for informational purposes.
Twisted Pair Cable
In twisted pair cables, each pair of wires in an ethernet cablevision is twisted. This is what information technology looks like inside the cable:
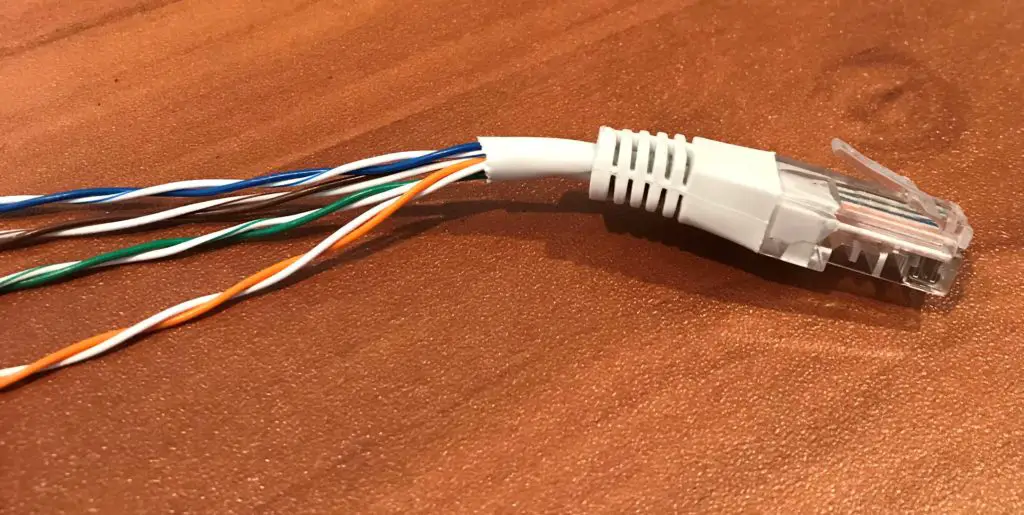

As you can see, the pairs of orange-white, light-green-white, brownish-white, and blueish-white are twisted within the ethernet cable.
Twisted pair cables will experience less crosstalk interference and therefore better performance. The twists in the wire pairs ensure that the electromagnetic forces in the twisted wires don't impact the other pairs in the cable.
Whatever ethernet cable you purchase today will be twisted pair assuming it is CAT5 or above.
When information technology comes to twisted pair cables, there are 2 types: shielded twisted pair (STP) and unshielded twisted pair (UTP)
Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) Cable
Some ethernet cables have a layer of foil wrapped effectually all the pairs of cables within it. Looking at the picture show below, you lot would see a foil wrapper effectually all the twisted pairs if it was a shielded cable.
The purpose of the shield is to prevent interference from the electric fields of nearby electronic devices (or the other wires in the cable). This volition meliorate operation, but information technology comes with a few drawbacks:
- Information technology is more expensive than unshielded cable
- Information technology is less flexible than shielded cable
- If there are no other electronic devices effectually causing interference, it is slower than unshielded cable
Shielded cable is best used in datacenters and other applications where it will be close to other electronic devices or cables.
Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Cablevision
Ethernet cables that are unshielded do not have foil around the pairs of twisted wires.
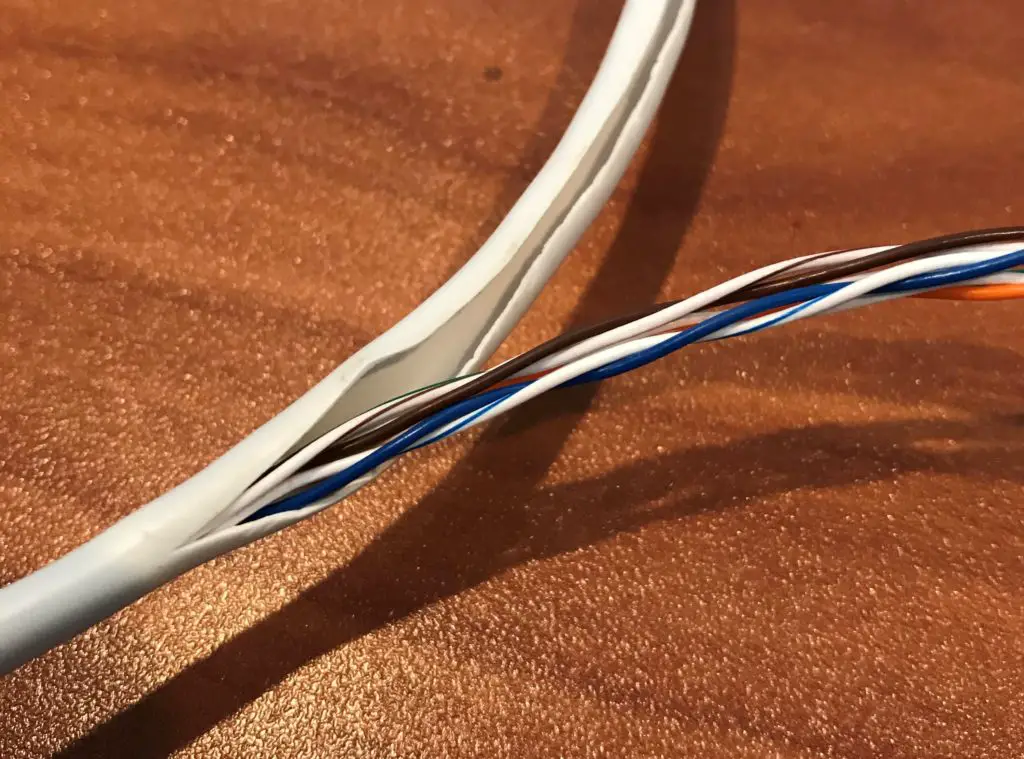

Equally you tin encounter, in that location are only twisted pairs of wires in the sheath.
In contrast to shielded cables, unshielded cables:
- Are cheaper
- Are more flexible
- Can be faster than shielded cables if there is no nearby electronic interference
In near home applications and offices (outside of the server room/datacenter), you will probably exist fine with unshielded cablevision.
How do I know what ethernet cable I have?
It is impossible to tell what kind of cables you have merely by looking at their appearance.
For case, look at his picture:
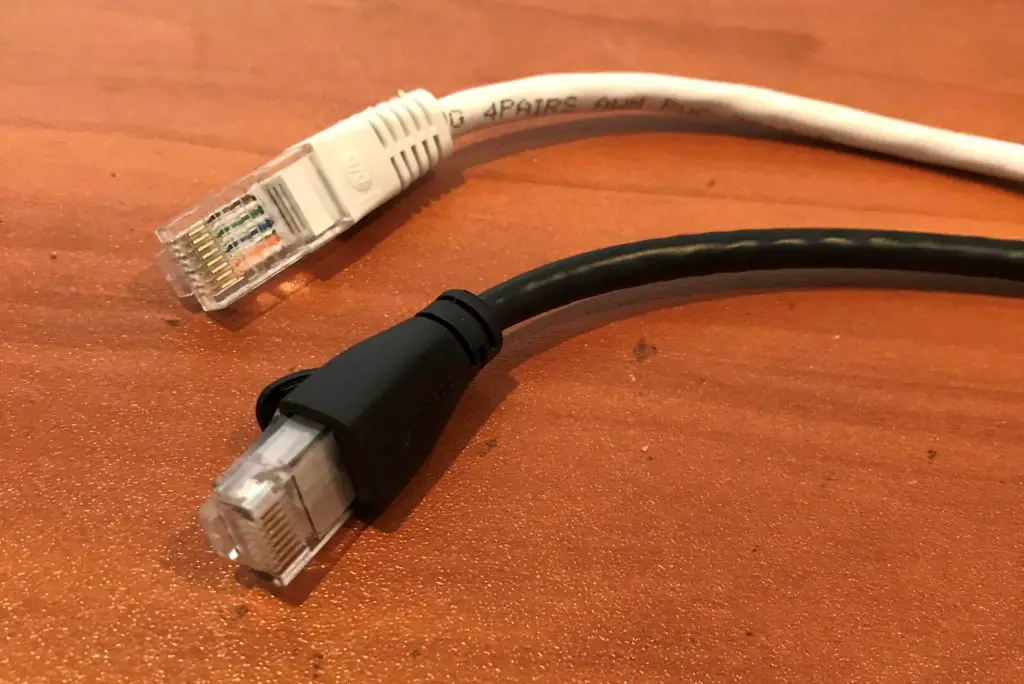

One of the cables is CAT5e and the other is CAT6. Tin can you tell which one is which?
The respond is no.
Thankfully, the ethernet cables take labels printed on their side to assist identify them.

As you can meet, the above cablevision is a CAT5e cable. What'due south more, you can see that the wires inside the cable are unshielded twisted pairs (UTP).
I recommend you double bank check all the ethernet cables in your network so you know what you accept. This volition give you an thought of what you need to replace also.
Does ethernet cable length affect internet speed?
The answer is no. In most cases you will non experience whatever loss in speed or reliability based upon the length of ethernet cable you get. You volition but take to worry near this if you are installing a network in a large office building where cables are longer than 100 meters.
This application is non the case for the majority of people. If you are looking to install longer runs of cable, you will be best suited using CAT6A cables (if they fit your data rate requirements).
What ethernet cables should I become?
My advice with ethernet cables would be to air on the side of caution.
For example if you take a dwelling house net plan with the following:
- 100 Mbps from the internet service provider
- A modem rated for 100 Mbps (or greater)
- A router rated for 100 Mbps (or greater)
- You will merely need shorter ethernet cables for your setup (less than 55 meters)
You should get either CAT5e or CAT6 cables.
Could CAT5 cables provide you with the speed y'all need? Most likely.
Would they allow you to upgrade your internet plan at any fourth dimension as they get faster and cheaper? No.
If you have a fiber internet plan with the following:
- 1,000 Mbps from the internet access provider
- A modem rated for one,000 Mbps (or greater)
- A router rated for 1,000 Mbps (or greater)
- You will only need shorter ethernet cables for your setup (less than 55 meters)
Y'all should get either CAT5e or CAT6 cables.
CAT5e and CAT6 cables are pretty cheap compared to your net plan. You should brand sure you build in room to upgrade your net without having to buy new cables as well.
This volition ensure that your often-overlooked ethernet cables are non the bottleneck of your cyberspace connection. Permit other people deal with that problem.
If you're looking to buy ethernet cables, I would recommend these Cat5e cables, or these Cat6 cables. You lot tin can get them in a variety of lengths and colors depending upon your habitation internet setup.
Wrap Up
As always, experience free to reach out to me via the Contact Me folio or the comments section beneath if you have any questions or you would like to share your experience.
If you would like to learn more than about how other aspects of your dwelling network could affect your cyberspace speed, check out our other posts on this topic:
Does Your Modem Affect Your Internet Speed?
Does a Router Affect Your WiFi Speed?
Is an Ethernet Cable Faster than WiFi?
Does an Former Calculator Affect Your Internet Speed?
Source: https://network-from-home.com/home-network/can-an-ethernet-cable-slow-your-internet-speed/
0 Response to "Does Cat6 Ethernet Cable Have Slow Upload Speeds?"
Post a Comment